Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Mesh a generic F1 car rear wing for external aero simulation#
Summary: This example demonstrates how to generate a mesh for a generic F1 rear wing STL file model.
Objective#
The example connects various parts of a rear wing from a generic F1 car
and volume meshes the resulting model using a poly-hexcore mesh containing prisms.
To simplify the process and enhance convenience, this example uses multiple
meshing utilities provided in the lucid class.
Procedure#
Launch an Ansys Prime Server instance.
Instantiate the meshing utilities from the
lucidclass.Import and append the STL geometry files for each part of the F1 rear wing.
Merge all imported components into a single part.
Use the connect operation to join the components together.
Define local size controls on aero surfaces.
Generate a surface mesh with curvature sizing.
Compute volume zones and define the fluid zone type.
Define the boundary layer.
Generate a volume mesh using poly-hexcore elements and apply boundary layer refinement.
Print statistics on the generated mesh.
Write a CAS file for use in the Fluent solver.
Exit the PyPrimeMesh session.
Launch Ansys Prime Server#
Import all necessary modules.
Launch an instance of Ansys Prime Server.
Connect the PyPrimeMesh client and get the model.
Instantiate meshing utilities from the lucid class.
import os
import tempfile
import ansys.meshing.prime as prime
from ansys.meshing.prime.graphics import PrimePlotter
prime_client = prime.launch_prime()
model = prime_client.model
mesh_util = prime.lucid.Mesh(model=model)
using server from docker : The container name ansys-prime-server-cb239931-f35d-4538-a61b-e2b69134bd43
Import geometry#
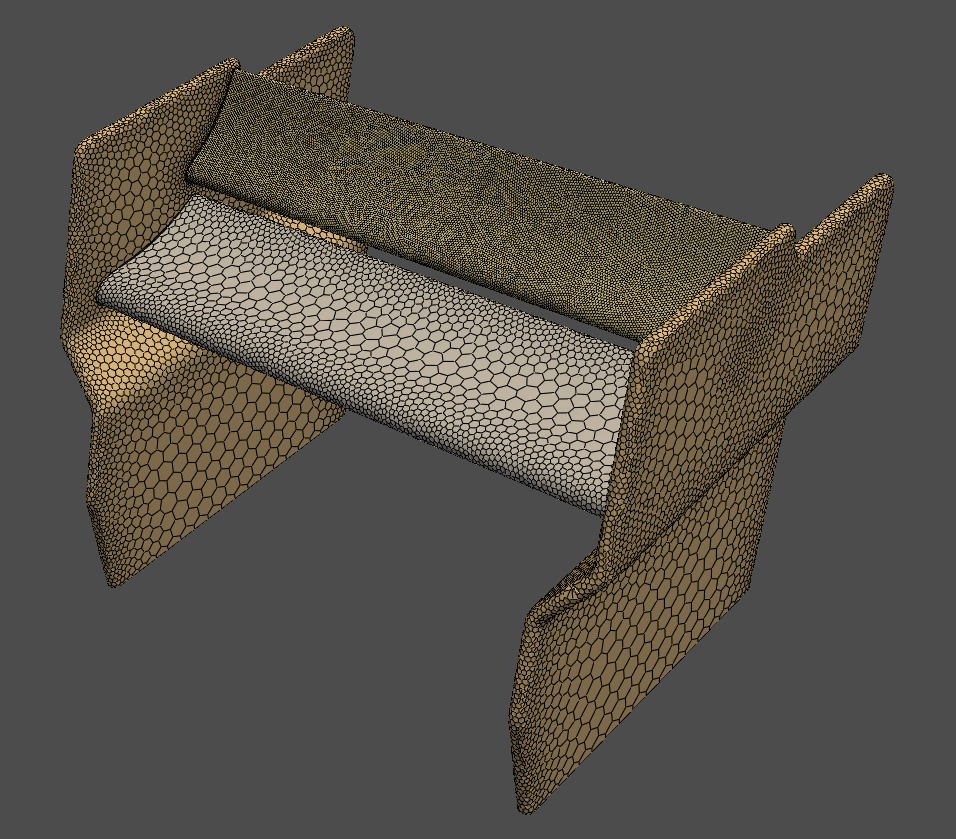
Download the generic F1 rear wing geometries (STL files). Import each geometry and append to the model. Display the imported geometry.
f1_rw_drs = prime.examples.download_f1_rw_drs_stl()
f1_rw_enclosure = prime.examples.download_f1_rw_enclosure_stl()
f1_rw_end_plates = prime.examples.download_f1_rw_end_plates_stl()
f1_rw_main_plane = prime.examples.download_f1_rw_main_plane_stl()
for file_name in [f1_rw_drs, f1_rw_enclosure, f1_rw_end_plates, f1_rw_main_plane]:
mesh_util.read(file_name, append=True)
# display the rear wing geometry without the enclosure
scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(model, part_expression="* !*enclosure*")
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, scope)
display.show()
Merge parts#
Establish the global size parameter to regulate mesh refinement.
Merge all individual parts into a unified part named f1_car_rear_wing.
# Define global sizes
model.set_global_sizing_params(prime.GlobalSizingParams(model, min=4, max=32, growth_rate=1.2))
# Create label per part
for part in model.parts:
part.add_labels_on_zonelets([part.name.split(".")[0]], part.get_face_zonelets())
# Merge parts
merge_params = prime.MergePartsParams(model, merged_part_suggested_name="f1_car_rear_wing")
merge_result = model.merge_parts([part.id for part in model.parts], merge_params)
part = model.get_part_by_name(merge_result.merged_part_assigned_name)
Mesh connect#
To generate a volume mesh for a closed domain, it is necessary to ensure that the components of the rear wing are properly connected. To achieve this, perform a connect operation using labels to join the components of the rear wing. Afterward, inspect the mesh to detect any edges that are not connected.
# Connect faces
mesh_util.connect_faces(part.name, face_labels="*", target_face_labels="*", tolerance=0.02)
# Diagnostics
surf_diag = prime.SurfaceSearch(model)
surf_report = surf_diag.get_surface_diagnostic_summary(
prime.SurfaceDiagnosticSummaryParams(
model,
compute_free_edges=True,
compute_self_intersections=True,
)
)
print(f"Total number of free edges present is {surf_report.n_free_edges}")
Total number of free edges present is 0
Define local size control and generate size-field#
To accurately represent the physics of the DRS wing, a limitation of 8 mm is imposed on the mesh size of the wing. This is accomplished by implementing a curvature size control, which refines the mesh according to the curvature of the DRS surfaces. Additionally, to accurately capture the curved surfaces of other sections of the wing, curvature control is defined with a normal angle of 18 degrees. These controls are used during surface mesh generation. A volumetric size field is then computed based on the defined size controls. The volumetric size field plays a crucial role in controlling the growth and refinement of the volume mesh.
# Local curvature size control for DRS
curv_size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.CURVATURE)
curv_size_params = prime.CurvatureSizingParams(model, normal_angle=18, max=4)
curv_size_control.set_curvature_sizing_params(curv_size_params)
curv_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(
model,
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.FACEZONELETS,
part_expression="f1_car_rear_wing*",
label_expression="*drs*",
)
curv_size_control.set_scope(curv_scope)
curv_size_control.set_suggested_name("curvature_drs")
# Global curvature size control on all face zones of the rear wing
curv_size_control_global = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.CURVATURE)
curv_size_params_global = prime.CurvatureSizingParams(model, normal_angle=18, min=8)
curv_size_control_global.set_curvature_sizing_params(curv_size_params_global)
curv_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(
model,
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.FACEZONELETS,
part_expression="f1_car_rear_wing*",
)
curv_size_control_global.set_scope(curv_scope)
curv_size_control_global.set_suggested_name("curvature_global")
# Compute volumetric sizefield
compute_size = prime.SizeField(model)
vol_sf_params = prime.VolumetricSizeFieldComputeParams(model)
compute_size.compute_volumetric(
[curv_size_control.id, curv_size_control_global.id], volumetric_sizefield_params=vol_sf_params
)
<ansys.meshing.prime.autogen.sizefieldstructs.VolumetricSizeFieldComputeResults object at 0x7f9a4ca6d090>
Generate surface mesh#
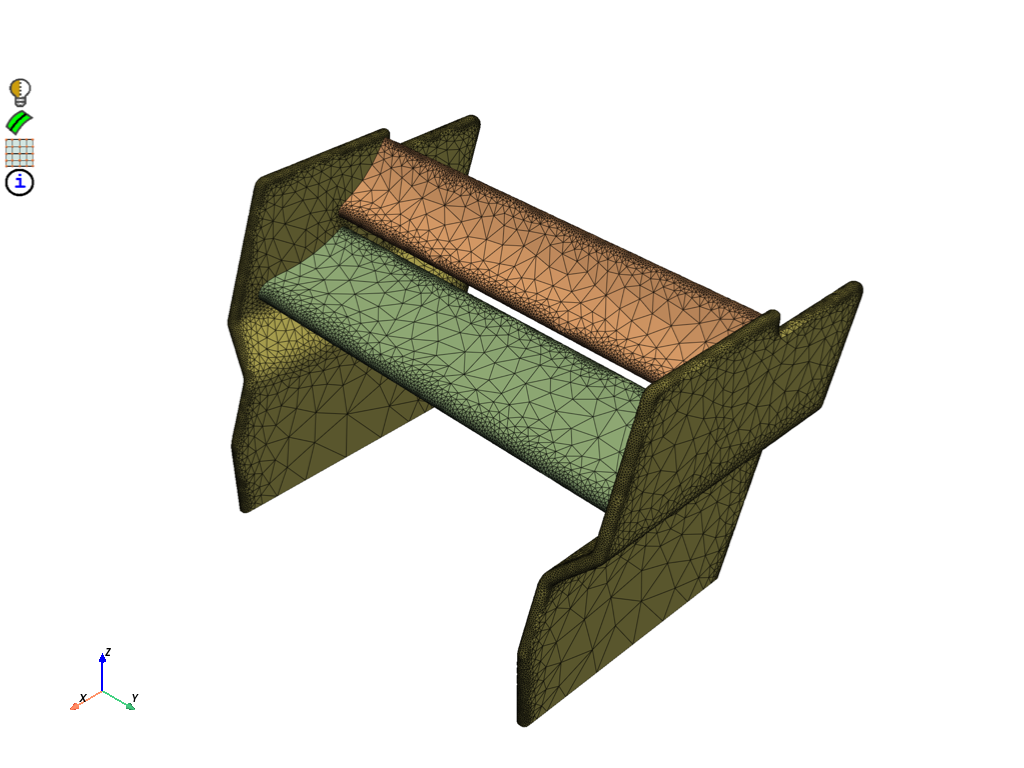
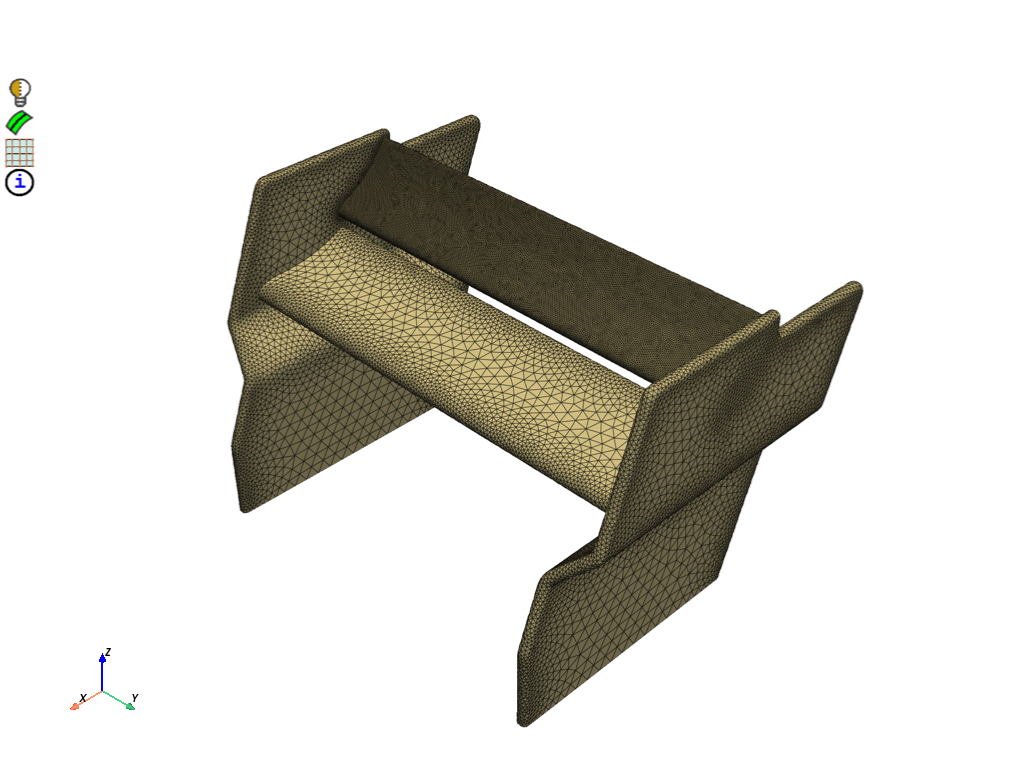
Create a surface mesh for the rear wing using the defined size controls. To facilitate the definition of boundary conditions on the surfaces in the solver, generate face zones by utilizing the existing labels found in the rear wing model.
mesh_util.surface_mesh_with_size_controls(size_control_names="*curvature*")
scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(model, label_expression="* !*enclosure*")
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, scope)
display.show()
# Create face zones per label
for label in part.get_labels():
mesh_util.create_zones_from_labels(label_expression=label)
Compute volumetric regions#
Compute the volume zones.
mesh_util.compute_volumes(part_expression=part.name, create_zones_per_volume=True)
Define volume controls#
To prevent the generation of a volume mesh within the solid wing,
the type of a volume zone within the rear wing can be defined as “dead.”
To accomplish this, Volume Control is utilized to assign the type for the
specific volume zone.
Expressions are employed to define the volume zones that need to be filled, with
* !f1_rw_enclosure indicating that it applies to all volume zones except
for f1_rw_enclosure.
volume_control = model.control_data.create_volume_control()
volume_control.set_params(
prime.VolumeControlParams(
model,
cell_zonelet_type=prime.CellZoneletType.DEAD,
)
)
volume_control.set_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model, evaluation_type=prime.ScopeEvaluationType.ZONES, zone_expression="* !f1_rw_enclosure"
)
)
<ansys.meshing.prime.autogen.controlstructs.SetScopeResults object at 0x7f9b092ed130>
Define prism controls#
A prism control can be used to define inflation layers on the external aero surfaces.
Specify the aero surfaces using labels. Here prism scope is defined on zones associated
with labels *drs* and *plane*.
The growth for the prism layer is controlled by defining the offset type to
be uniform with a first height of 0.5mm .
prism_control = model.control_data.create_prism_control()
prism_control.set_surface_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model,
evaluation_type=prime.ScopeEvaluationType.LABELS,
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.FACEZONELETS,
label_expression="*drs*, *plane*",
)
)
prism_control.set_volume_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model,
evaluation_type=prime.ScopeEvaluationType.ZONES,
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.VOLUME,
zone_expression="*f1_rw_enclosure*",
)
)
prism_control.set_growth_params(
prime.PrismControlGrowthParams(
model,
offset_type=prime.PrismControlOffsetType.UNIFORM,
n_layers=5,
first_height=0.5,
growth_rate=1.2,
)
)
Generate volume mesh#
Volume mesh with hexcore polyhedral elements and boundary layer refinement.
volume_mesh = prime.AutoMesh(model)
auto_mesh_param = prime.AutoMeshParams(
model,
prism_control_ids=[prism_control.id],
size_field_type=prime.SizeFieldType.VOLUMETRIC,
volume_fill_type=prime.VolumeFillType.HEXCOREPOLY,
volume_control_ids=[volume_control.id],
)
volume_mesh.mesh(part.id, auto_mesh_param)
<ansys.meshing.prime.autogen.automeshstructs.AutoMeshResults object at 0x7f9a4ca6d090>
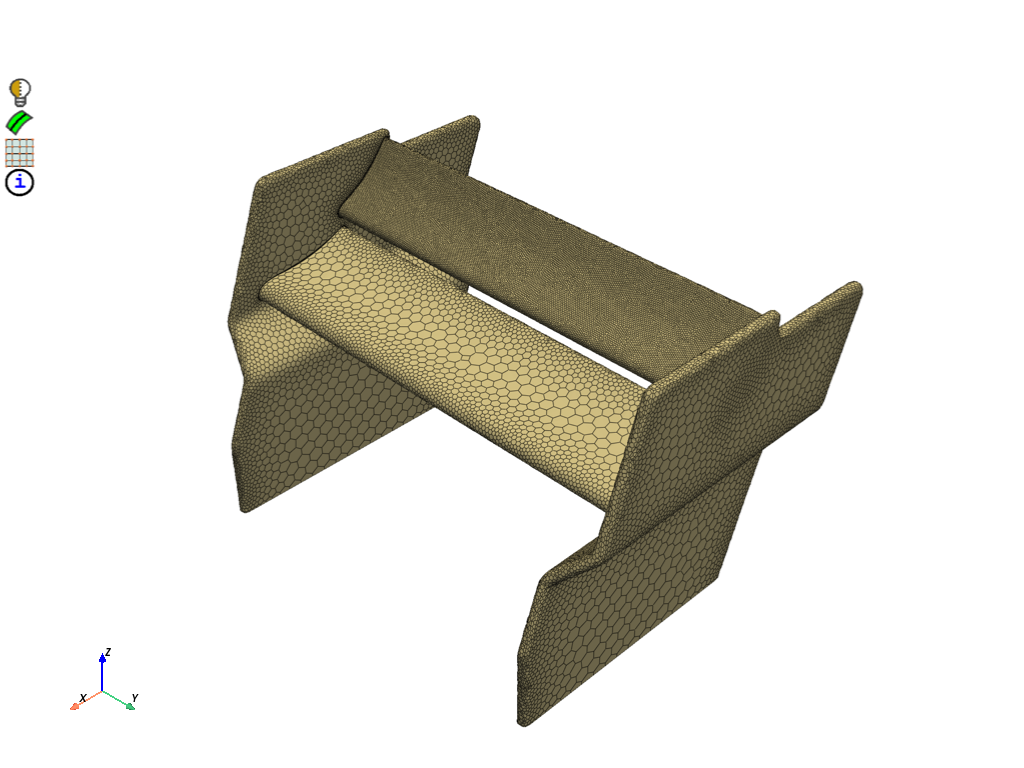
Print mesh statistics#
# Get meshed part
part = model.get_part_by_name("f1_car_rear_wing")
# Get statistics on the mesh
part_summary_res = part.get_summary(prime.PartSummaryParams(model=model))
# Get element quality on all parts in the model
search = prime.VolumeSearch(model=model)
params = prime.VolumeQualitySummaryParams(
model=model,
scope=prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model, part_expression="*"),
cell_quality_measures=[prime.CellQualityMeasure.INVERSEORTHOGONAL],
quality_limit=[0.9],
)
results = search.get_volume_quality_summary(params=params)
# Print statistics on meshed part
print(part_summary_res)
print(
"\nMaximum inverse-orthoginal quality of the volume mesh : ",
results.quality_results_part[0].max_quality,
)
# Mesh check
result = prime.VolumeMeshTool(model).check_mesh(part.id, params=prime.CheckMeshParams(model))
print("\nMesh check", result, sep="\n")
scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(model, part_expression="*", label_expression="* !*enclosure*")
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, scope, update=True)
display.show()
message :
Part Name: f1_car_rear_wing
Part ID: 6
0 Edge Zonelets
4 Face Zonelets
1 Cell Zonelets
0 Edge Zones
Edge Zone Name(s) : []
4 Face Zones
Face Zone Name(s) : [f1_rw_drs.1, f1_rw_enclosure.1, f1_rw_end_plates.1, f1_rw_main_plane.1]
2 Volume Zones
Volume Zone Name(s) : [f1_rw_enclosure, f1_rw_end_plates]
4 Label(s)
Names: [f1_rw_drs, f1_rw_enclosure, f1_rw_end_plates, f1_rw_main_plane]
Bounding box (-1500 -900 -300)
(500 900 1200)
Mesh Summary:
1604547 Nodes
73398 Poly Faces
0 Quad Faces
0 Tri Faces
73398 Faces
589375 Poly Cells
0 Hex Cells
0 Prism Cells
0 Pyramid Cells
0 Tet Cells
589375 Cells
n_topo_edges : 0
n_topo_faces : 0
n_topo_volumes : 0
n_edge_zonelets : 0
n_face_zonelets : 4
n_cell_zonelets : 1
n_edge_zones : 0
n_face_zones : 4
n_volume_zones : 2
n_labels : 4
n_nodes : 1604547
n_faces : 73398
n_cells : 589375
n_tri_faces : 0
n_poly_faces : 73398
n_quad_faces : 0
n_second_order_tri_faces : 0
n_second_order_quad_faces : 0
n_tet_cells : 0
n_pyra_cells : 0
n_prism_cells : 0
n_poly_cells : 589375
n_hex_cells : 0
n_second_order_tet_cells : 0
n_second_order_pyra_cells : 0
n_second_order_prism_cells : 0
n_second_order_hex_cells : 0
n_unmeshed_topo_faces : 0
Maximum inverse-orthoginal quality of the volume mesh : 0.868199
Mesh check
has_non_positive_volumes : False
has_non_positive_areas : False
has_invalid_shape : False
has_left_handed_faces : False
error_code : 0
warning_codes : []
Write mesh#
Export as CAS file for external aero simulations.
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_folder:
print(temp_folder)
mesh_file = os.path.join(temp_folder, "f1_rear_wing_vol_mesh.cas")
mesh_util.write(mesh_file)
assert os.path.exists(mesh_file)
print("\nExported file:\n", mesh_file)
/tmp/tmp0h1qmgs6
Exported file:
/tmp/tmp0h1qmgs6/f1_rear_wing_vol_mesh.cas
Exit PyPrimeMesh#
prime_client.exit()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 34.097 seconds)

