Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Mesh a saddle bracket for a structural analysis#
Summary: This example demonstrates how to mesh a thin solid with hexahedral and prism cells.
Objective#
This example creates a mainly hexahedral mesh on a thin solid volume.
Procedure#
Launch Ansys Prime Server.
Import the CAD geometry.
Quad surface mesh the source face.
Surface mesh the remaining unmeshed TopoFaces with tri surface mesh.
Delete the topology.
Define volume meshing controls to use thin volume meshing.
Volume mesh with hexahedral and prism cells.
Write a CDB file for use in the APDL solver.
Exit the PyPrimeMesh session.
Launch Ansys Prime Server#
Import all necessary modules. Launch an instance of Ansys Prime Server. Connect the PyPrimeMesh client and get the model.
import os
import tempfile
import ansys.meshing.prime as prime
from ansys.meshing.prime.graphics import PrimePlotter
prime_client = prime.launch_prime()
model = prime_client.model
mesh_util = prime.lucid.Mesh(model)
using server from docker : The container name ansys-prime-server-5e21275e-b47f-4819-a762-8da85b601342
Import geometry#
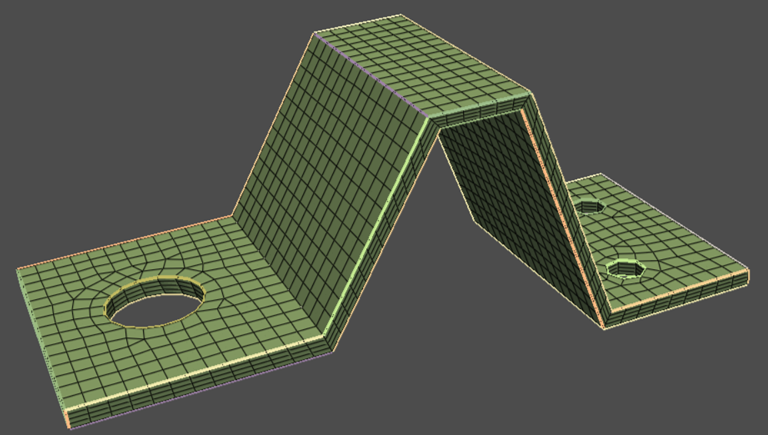
Download the saddle bracket geometry (FMD) file exported by SpaceClaim. Import the geometry and display all.
# For Windows OS users, scdoc is also available:
# saddle_bracket = prime.examples.download_saddle_bracket_scdoc()
saddle_bracket = prime.examples.download_saddle_bracket_fmd()
mesh_util.read(file_name=saddle_bracket)
print(model)
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model)
display.show()
Part Summary:
Part Name: saddle_bracket
Part ID: 2
42 Topo Edges
17 Topo Faces
1 Topo Volumes
0 Edge Zones
Edge Zone Name(s) : []
0 Face Zones
Face Zone Name(s) : []
1 Volume Zones
Volume Zone Name(s) : [solid]
12 Label(s)
Names: [hole1, hole2, hole3, round_group1, round_group2, round_group4, round_group5, round_group6, round_group7, round_group8, source_thin, target_thin]
Bounding box (-27.3636 -0.62 -21.923)
(46.7236 27.82 7.62845)
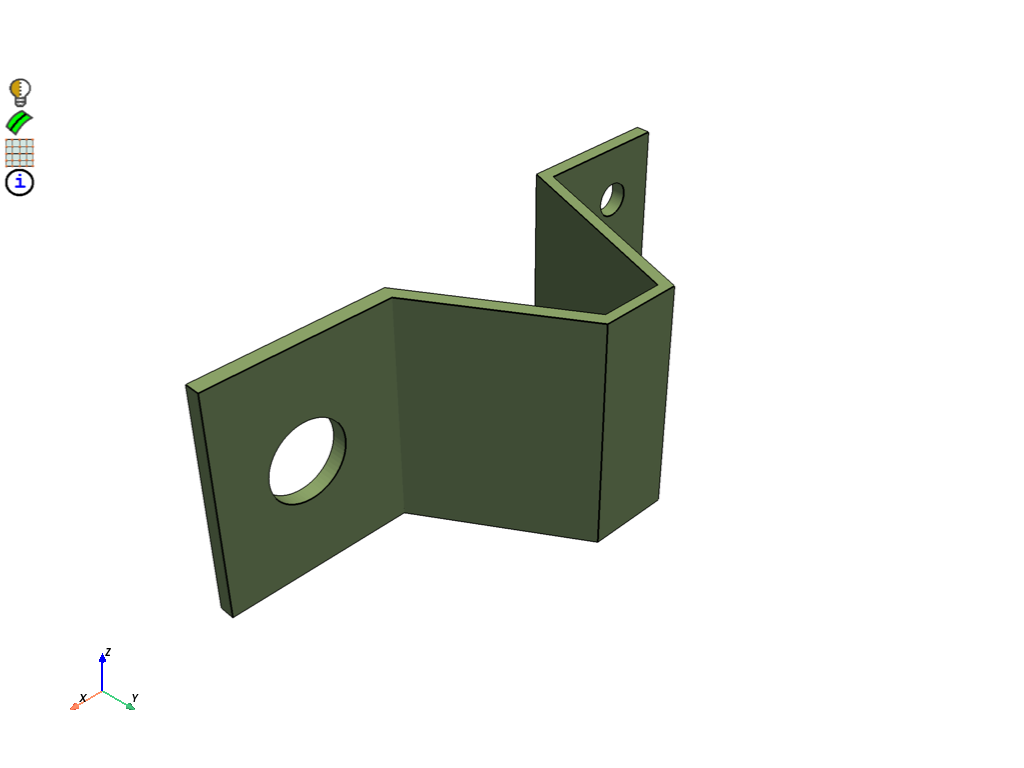
Quad mesh source faces#
Mesh the source faces for the thin volume control with quads.
scope = prime.lucid.SurfaceScope(
part_expression="*",
entity_expression="source_thin",
scope_evaluation_type=prime.ScopeEvaluationType.LABELS,
)
mesh_util.surface_mesh(
scope=scope,
min_size=2.0,
generate_quads=True,
)
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, update=True)
display.show()
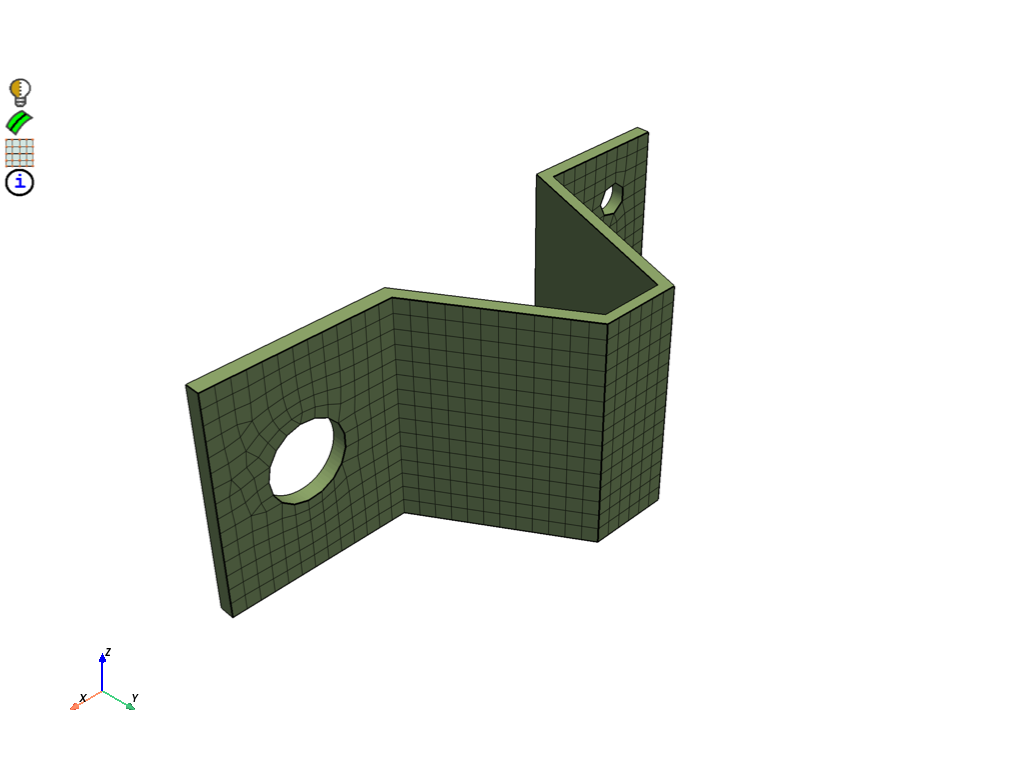
Surface mesh unmeshed faces#
Mesh unmeshed faces with tri surface mesh. Tri surface mesh on the target and side faces is used to show more clearly that the result of the thin volume control is a hex mesh that is imprinted up to the side faces. All quads could be used for the surface mesh to simplify the process.
part = model.parts[0]
all_faces = part.get_topo_faces()
meshed_faces = part.get_topo_faces_of_label_name_pattern(
label_name_pattern="source_thin",
name_pattern_params=prime.NamePatternParams(model),
)
unmeshed_faces = [face for face in all_faces if face not in meshed_faces]
part.add_labels_on_topo_entities(
labels=["unmeshed_faces"],
topo_entities=unmeshed_faces,
)
scope = prime.lucid.SurfaceScope(
part_expression="*",
entity_expression="unmeshed_faces",
scope_evaluation_type=prime.ScopeEvaluationType.LABELS,
)
mesh_util.surface_mesh(
scope=scope,
min_size=2.0,
)
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, update=True)
display.show()
Delete topology#
Delete topology to leave only the surface mesh. This is necessary for the thin volume control to be used.
part.delete_topo_entities(
prime.DeleteTopoEntitiesParams(
model=model,
delete_geom_zonelets=True,
delete_mesh_zonelets=False,
)
)
<ansys.meshing.prime.autogen.partstructs.DeleteTopoEntitiesResults object at 0x7fe9602fe490>
Define volume meshing controls#
Define volume meshing controls to use thin volume meshing.
Specify source and target faces for the thin volume using imported labels.
Set the number of layers of cells through the thickness of the thin solid to be 4.
To create a fully hexahedral and prism mesh the side faces must be imprinted on
the side faces. If needed, a buffer region at the sides of the volume can be
defined where the volume fill type used for the volume mesh parameters is
used to infill. This is useful on more complex geometries, where it provides
more robustness of the method. To create a buffer region set imprint_sides
to False and specify how many rings of cells to ignore at the sides
using n_ignore_rings.
auto_mesh_params = prime.AutoMeshParams(model=model)
thin_vol_ctrls_ids = []
thin_vol_ctrl = model.control_data.create_thin_volume_control()
thin_vol_ctrl.set_source_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
label_expression="source_thin",
)
)
thin_vol_ctrl.set_target_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
label_expression="target_thin",
)
)
thin_params = prime.ThinVolumeMeshParams(
model=model,
n_layers=4,
imprint_sides=True,
)
thin_vol_ctrl.set_thin_volume_mesh_params(thin_volume_mesh_params=thin_params)
thin_vol_ctrls_ids.append(thin_vol_ctrl.id)
auto_mesh_params.thin_volume_control_ids = thin_vol_ctrls_ids
auto_mesh_params.volume_fill_type = prime.VolumeFillType.TET
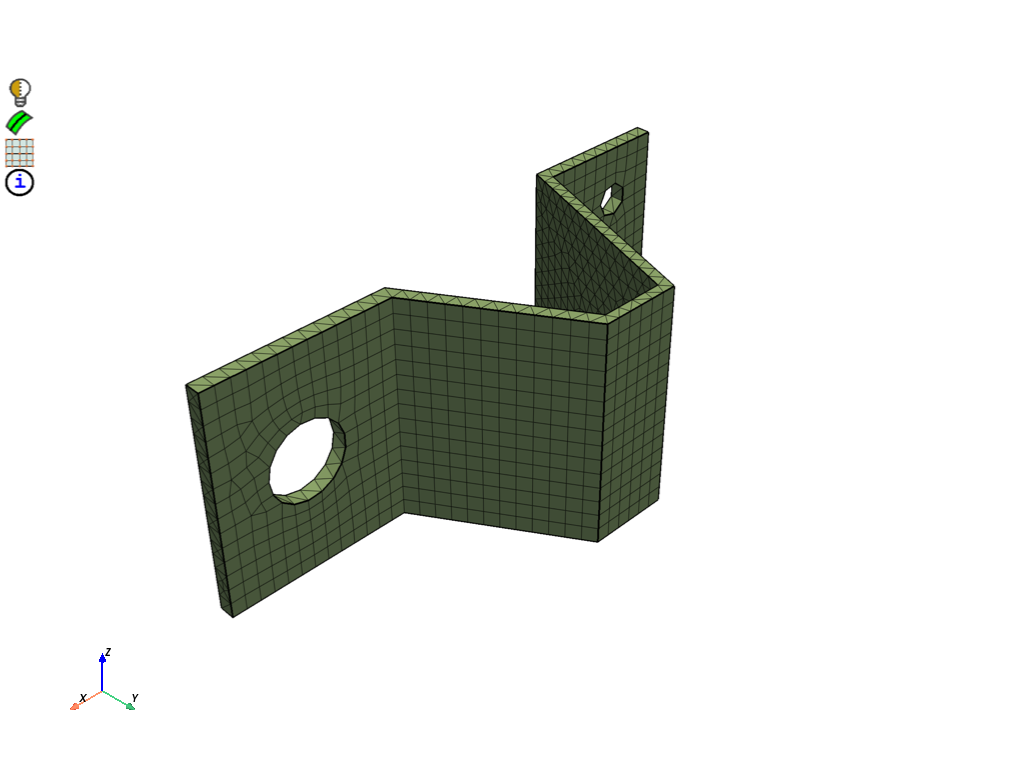
Generate volume mesh#
Volume mesh to obtain hexahedral and prism mesh. Print mesh summary. Display volume mesh.
volume_mesh = prime.AutoMesh(model=model)
result_vol = volume_mesh.mesh(part_id=part.id, automesh_params=auto_mesh_params)
print(part.get_summary(prime.PartSummaryParams(model)))
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, update=True)
display.show()
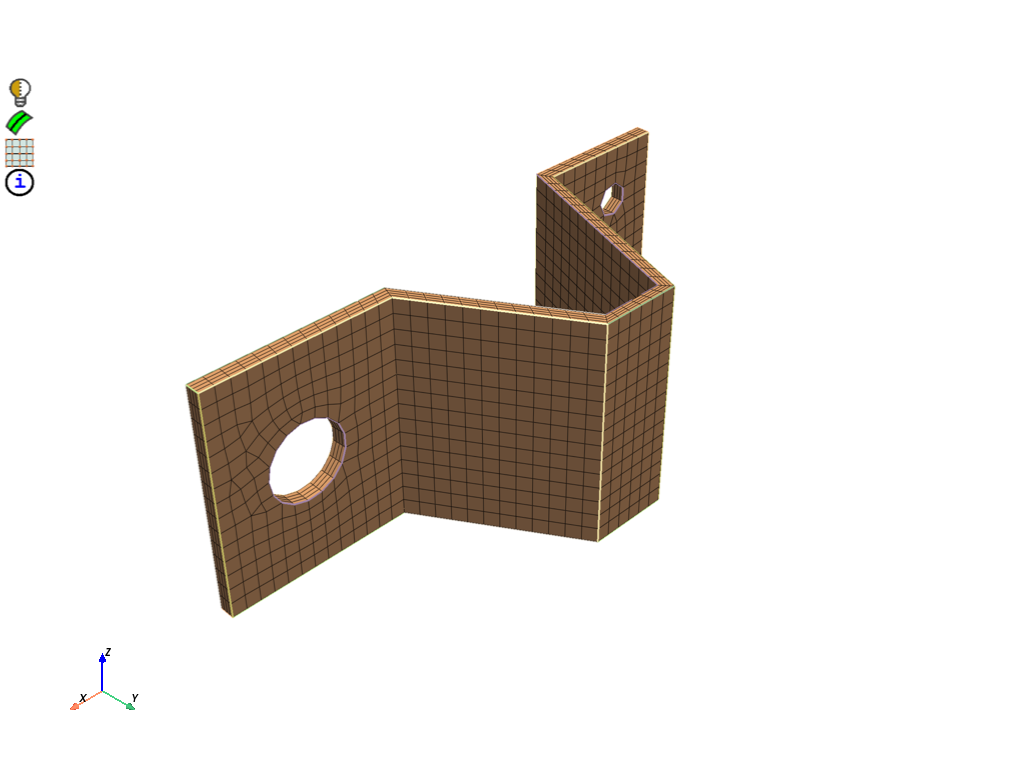
message :
Part Name: saddle_bracket
Part ID: 2
42 Edge Zonelets
17 Face Zonelets
1 Cell Zonelets
0 Edge Zones
Edge Zone Name(s) : []
0 Face Zones
Face Zone Name(s) : []
1 Volume Zones
Volume Zone Name(s) : [solid]
13 Label(s)
Names: [hole1, hole2, hole3, round_group1, round_group2, round_group4, round_group5, round_group6, round_group7, round_group8, source_thin, target_thin, unmeshed_faces]
Bounding box (-27.3636 -0.62 -21.923)
(46.7236 27.82 7.62845)
Mesh Summary:
4640 Nodes
0 Poly Faces
2266 Quad Faces
26 Tri Faces
2292 Faces
0 Poly Cells
3180 Hex Cells
52 Prism Cells
0 Pyramid Cells
0 Tet Cells
3232 Cells
n_topo_edges : 0
n_topo_faces : 0
n_topo_volumes : 0
n_edge_zonelets : 42
n_face_zonelets : 17
n_cell_zonelets : 1
n_edge_zones : 0
n_face_zones : 0
n_volume_zones : 1
n_labels : 13
n_nodes : 4640
n_faces : 2292
n_cells : 3232
n_tri_faces : 26
n_poly_faces : 0
n_quad_faces : 2266
n_second_order_tri_faces : 0
n_second_order_quad_faces : 0
n_tet_cells : 0
n_pyra_cells : 0
n_prism_cells : 52
n_poly_cells : 0
n_hex_cells : 3180
n_second_order_tet_cells : 0
n_second_order_pyra_cells : 0
n_second_order_prism_cells : 0
n_second_order_hex_cells : 0
n_unmeshed_topo_faces : 0
Write mesh#
Write a CDB file for use in the MAPDL solver.
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_folder:
mesh_file = os.path.join(temp_folder, "saddle_bracket.cdb")
mesh_util.write(mesh_file)
assert os.path.exists(mesh_file)
print("\nExported file:\n", mesh_file)
This get_abaqus_simulation_data is a beta API. The behavior and implementation may change in future.
/home/runner/work/pyprimemesh/pyprimemesh/.venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/ansys/meshing/prime/core/fileio.py:339: PrimeRuntimeWarning: Skipped the export of label as element component because the labelled topology or zonelets are not a part of any zone. Refer label_export_params to export desired labels as nodal components.
result = super().export_mapdl_cdb(temp_file_name, params)
Exported file:
/tmp/tmpxooud5hc/saddle_bracket.cdb
Exit PyPrimeMesh#
prime_client.exit()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 27.925 seconds)

