Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Morph a hexahedral mesh of a turbine blade to a new shape#
Summary: This example demonstrates how to morph a structural hexahedral mesh of a turbine blade to a new deformed shape defined by a target geometry file.
Objective#
This example appends a CDB mesh with a CAD geometry and match morphs the mesh to the geometry.
Procedure#
Launch an Ansys Prime Server instance and connect the PyPrimeMesh client.
Read the mesh and append the new CAD geometry shape.
Define the mesh source faces and the target geometry faces to match morph.
Match morph the turbine blade mesh to the new CAD geometry shape.
Write the mesh for structural analysis.
Launch Ansys Prime Server#
Import all necessary modules.
Launch the Ansys Prime Server instance and connect the client.
Get the client model and instantiate meshing utilities from the lucid class.
import os
import tempfile
import ansys.meshing.prime as prime
from ansys.meshing.prime.graphics import PrimePlotter
prime_client = prime.launch_prime()
model = prime_client.model
mesh_util = prime.lucid.Mesh(model=model)
using server from docker : The container name ansys-prime-server-feb79d61-cc87-45d2-9330-ca537c09d0ed
Read files#
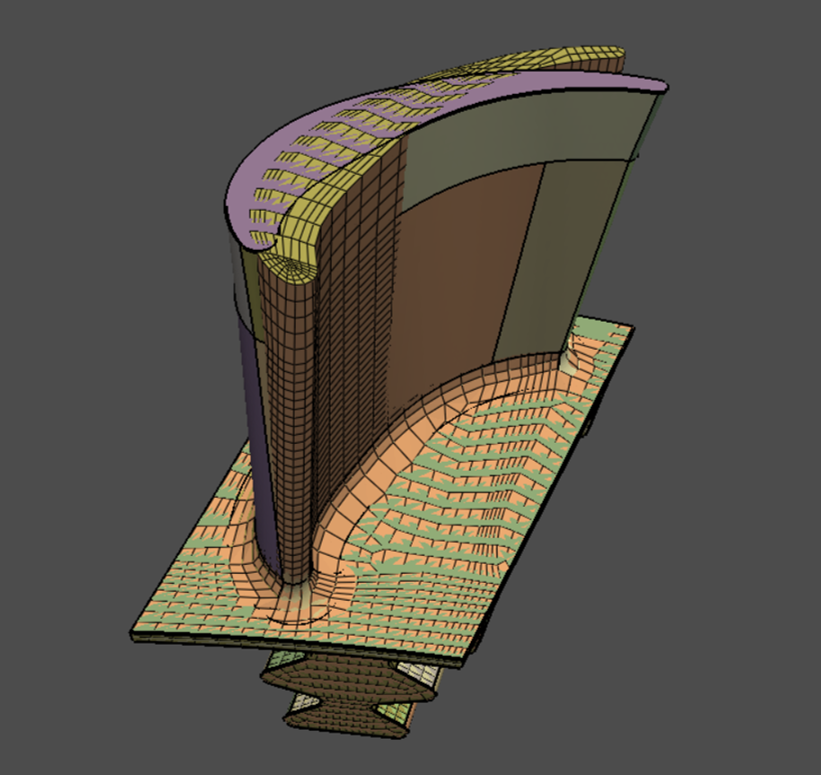
Download the turbine blade mesh file and CAD geometry. Read the mesh and append the geometry. Display the source and the target.
# For Windows OS users, scdoc is also available for geometry:
# target_geometry = prime.examples.download_turbine_blade_target_scdoc()
source_mesh = prime.examples.download_turbine_blade_cdb()
target_geometry = prime.examples.download_deformed_blade_fmd()
mesh_util.read(file_name=source_mesh)
mesh_util.read(file_name=target_geometry, append=True)
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model)
display.show()
print(model)
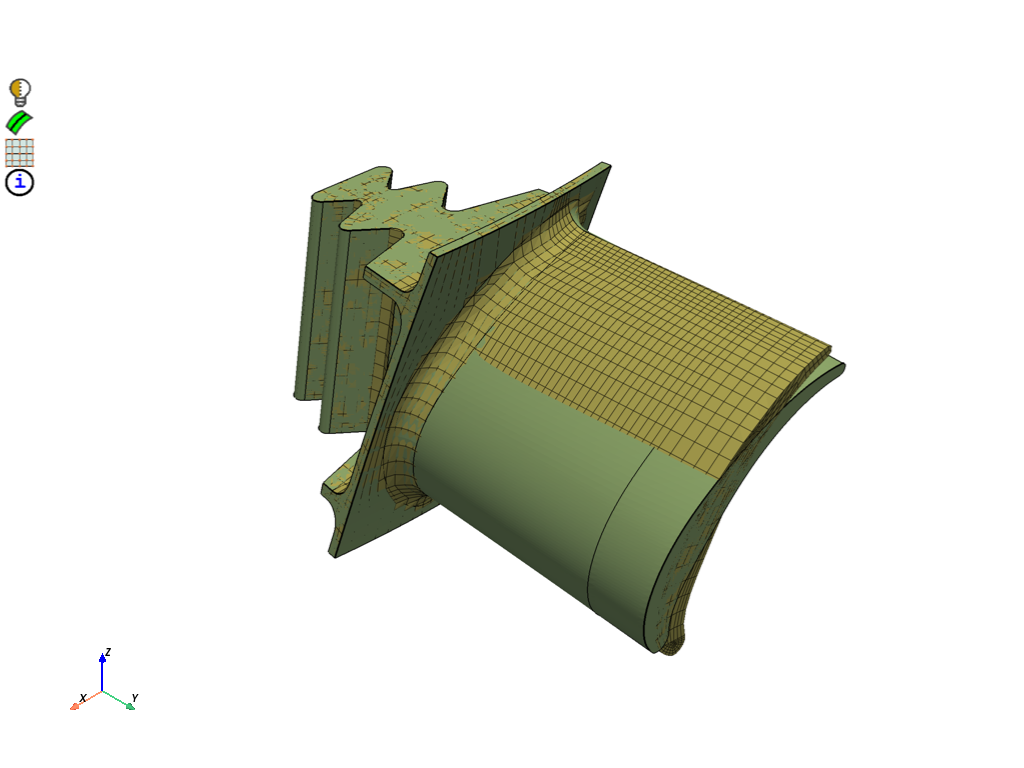
Part Summary:
Part Name: blade
Part ID: 2
0 Edge Zonelets
6 Face Zonelets
1 Cell Zonelets
0 Edge Zones
Edge Zone Name(s) : []
0 Face Zones
Face Zone Name(s) : []
1 Volume Zones
Volume Zone Name(s) : [volume]
5 Label(s)
Names: [FIRTREE1, FIRTREE2, FIRTREE3, FIRTREE4, PRESSURE_SURF]
Bounding box (-0.781465 4.39775 -0.7)
(0.79353 6.8 0.7)
Part Name: blade_deformed
Part ID: 3
202 Topo Edges
80 Topo Faces
1 Topo Volumes
0 Edge Zones
Edge Zone Name(s) : []
0 Face Zones
Face Zone Name(s) : []
1 Volume Zones
Volume Zone Name(s) : [solid]
0 Label(s)
Names: []
Bounding box (-0.781465 4.39775 -0.7)
(0.79353 6.8 0.7)
Define source and target faces#
Match morph mesh#
Set the target type to be for topoface because the target is geometry.
Morph the source face zonelets of source_part to the
target topofaces of the geometry.
morpher = prime.Morpher(model)
match_pair = prime.MatchPair(
model=model,
source_surfaces=source,
target_surfaces=target,
target_type=prime.MatchPairTargetType.TOPOFACE,
)
params = prime.MatchMorphParams(model)
bc_params = prime.MorphBCParams(model)
solver_params = prime.MorphSolveParams(model)
morpher.match_morph(
part_id=source_part.id,
match_pairs=[match_pair],
match_morph_params=params,
bc_params=bc_params,
solve_params=solver_params,
)
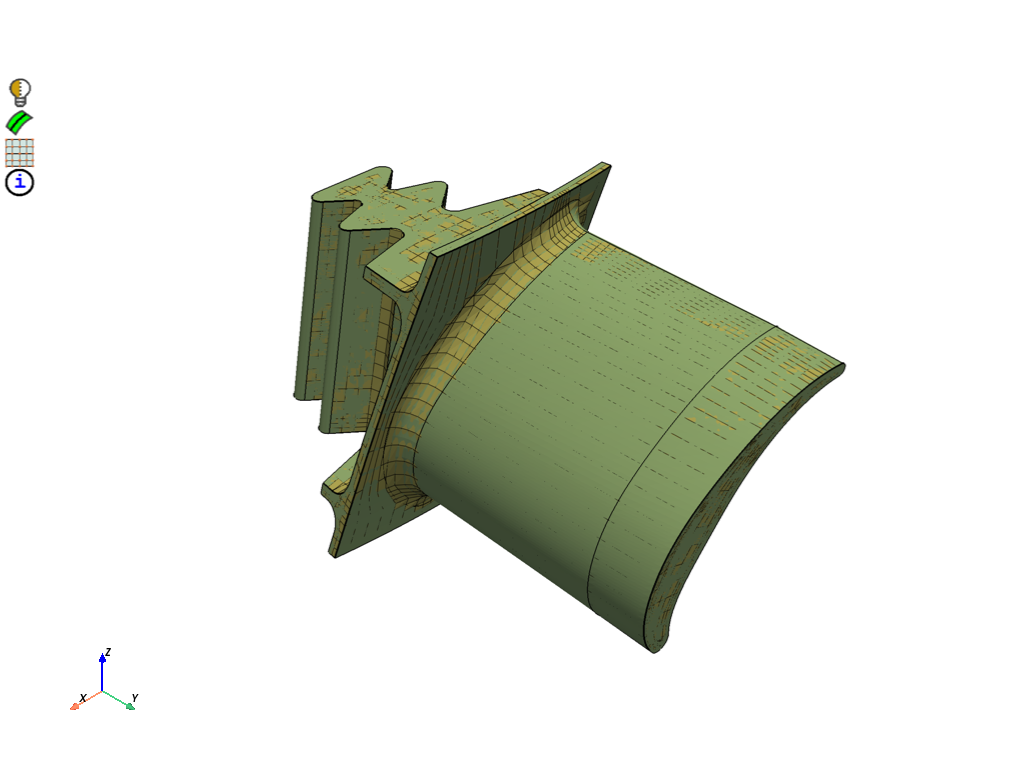
# Display the morphed mesh
display = PrimePlotter()
display.plot(model, update=True)
display.show()
Write mesh#
Write the morphed CDB file. The geometry is ignored when exporting to a CDB file.
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_folder:
mesh_file = os.path.join(temp_folder, "morphed_turbine_blade.cdb")
mesh_util.write(mesh_file)
assert os.path.exists(mesh_file)
print("\nExported file:\n", mesh_file)
This get_abaqus_simulation_data is a beta API. The behavior and implementation may change in future.
Exported file:
/tmp/tmpoz5fqip_/morphed_turbine_blade.cdb
Exit PyPrimeMesh#
prime_client.exit()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 5.121 seconds)

