Reading and writing files#
The FileIO class is used for all file-based data exchanges.
Native PMDAT format#
PMDAT is the native file format for PyPrimeMesh. It contains all data associated with the active model.
This includes geometry, mesh, topology, controls, labels, and zones.
The model data can be read from and written to the PMDAT format using the
FileIO.read_pmdat() and
FileIO.write_pmdat() methods
with parameters defined in the FileReadParams
and FileWriteParams classes respectively.
from ansys.meshing import prime
# Start Ansys Prime Server and get the model
prime_client = prime.launch_prime()
model = prime_client.model
# Download and read an example PMDAT file
mixing_elbow = prime.examples.download_elbow_pmdat()
params = prime.FileReadParams(model=model)
prime.FileIO(model).read_pmdat(file_name=mixing_elbow, file_read_params=params)
Tip
Files can be read or imported based on file extension using the Mesh.read()
method in the Lucid API. The method supports PyPrimeMesh’s native format, various CAD formats, and solver mesh files.
Import CAD files#
The FileIO.import_cad() method allows
you to import CAD files and set parameters for importing files using the
ImportCadParams class.
CAD reader routes#
You can specify the import route for CAD files using the CadReaderRoute class.
params = prime.ImportCadParams(
model=model, cad_reader_route=prime.CadReaderRoute.DISCOVERY
)
prime.FileIO(model).import_cad(file_name=mixing_elbow, params=params)
Alternatively, you can use the Mesh class in the Lucid API:
mesh_util = prime.lucid.Mesh(model=model)
mesh_util.read(file_name=mixing_elbow, cad_reader_route=prime.CadReaderRoute.DISCOVERY)
Five CAD import routes are available in PyPrimeMesh:
Program controlled: Chooses the CAD reader route based on the extension of the provided CAD file as follows:
Native for FMD, X_T, X_B, JT, PLMXML, and STL
Discovery for DSCO, SCDOC and SCDOCX
Workbench for all other extensions
Native: Natively supported file format extensions are FMD, Parasolid (X_T and X_B), JTOpen (JT and PLMXML), and STL.
SpaceClaim: Uses SpaceClaim to import supported CAD files from the SpaceClaim reader. Only the Windows platform supports importing files using the SpaceClaim reader. Ensure to install SpaceClaim for SpaceClaim reader.
Discovery: Uses Discovery to import supported CAD files from the Discovery reader. Only the Windows platform supports importing files using the Discovery reader. Ensure to install Discovery for Discovery reader.
Workbench: Uses Workbench to import supported CAD files from the Workbench reader. Ensure to install Workbench for Workbench reader.
To view the CAD files supported for the Workbench route on different platforms, see CAD Support on the Ansys website.
Note
Program controlled supports faceted data. Workbench supports BRep geometry(non-faceted) data. Discovery or SpaceClaim supports both BRep geometry and faceted data.
When deploying scripts using the Workbench CAD reader route, ensure that the user options for the installed application are consistent in the deployed environment.
When deploying scripts using the CAD configuration, ensure that the configuration is consistent in the deployed environment.
You must install and configure Workbench CAD readers or plug-ins (Ansys Geometry Interfaces) while installing Ansys Workbench.
To preserve shared topology, the Workbench CAD reader route must be used.
Patterned name selections are not supported for the SpaceClaim or Discovery CAD reader routes. To import patterned named selections, the Workbench CAD reader route can be used.
Append CAD files#
The ImportCadParams.append parameter allows
you to append a CAD file to the model:
params = prime.ImportCadParams(model=model, append=True)
prime.FileIO(model).import_cad(file_name="cad_to_append.dsco", params=params)
Alternatively, you can use the Mesh class in
the Lucid API:
mesh_util = prime.lucid.Mesh(model=model)
mesh_util.read("cad_to_append.dsco", append=True)
Parametric CAD update#
Parametric CAD update can be used while importing CAD files that have parameters defined that can be accessed by Workbench CAD readers.
This code gets existing CAD parameters while importing:
params = prime.ImportCadParams(model=model)
params.cad_reader_route = prime.CadReaderRoute.WORKBENCH
result = prime.FileIO(model).import_cad(file_name="parametric_cad.dsco", params=params)
>>> print(result.cad_parameters)
{'my_param': 1}
This code sets the parameters that are used for the import:
params = prime.ImportCadParams(model=model)
params.cad_reader_route = prime.CadReaderRoute.WORKBENCH
params.cad_update_parameters = {"my_param": 2}
result = prime.FileIO(model).import_cad(file_name="parametric_cad.dsco", params=params)
>>> print(result.cad_parameters)
{'my_param': 2}
Part management and creation#
PyPrimeMesh has options for part management within the product structure while importing a CAD (Computer Aided Design) model. The CAD model is the top in product hierarchy. A CAD model can have one or more CAD assemblies. The CAD assembly or subassembly has different CAD parts. The CAD part has bodies or other geometric entities. Here is a typical CAD product structure from SpaceClaim:
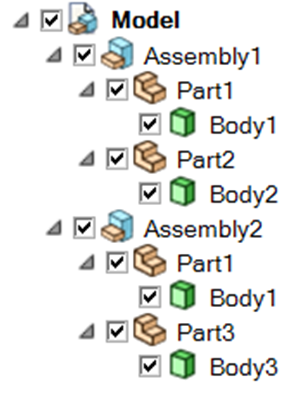
Example CAD structure from SpaceClaim#
The PartCreationType class decides whether to create a part per:
Model
Assembly
Part
Body
Model#
When you import a CAD model and specify the PartCreationType parameter
as MODEL, a single part is created that inherits its name from
the CAD model name. The number of zones within the part is identical to the number of bodies within the CAD model.
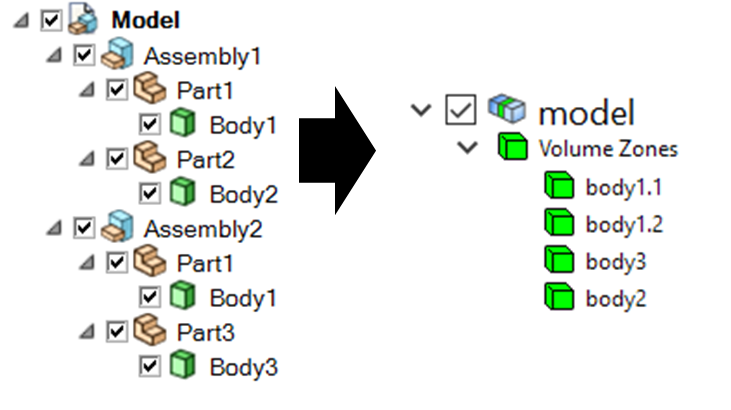
Part creation by model (from SpaceClaim to PyPrimeMesh part structure)#
Assembly#
When you import a CAD model and specify the PartCreationType parameter
as ASSEMBLY, a part per CAD assembly is created where the part
name is inherited from the CAD assembly name. The number of zones within each part is identical to the number of bodies
within the CAD assembly.
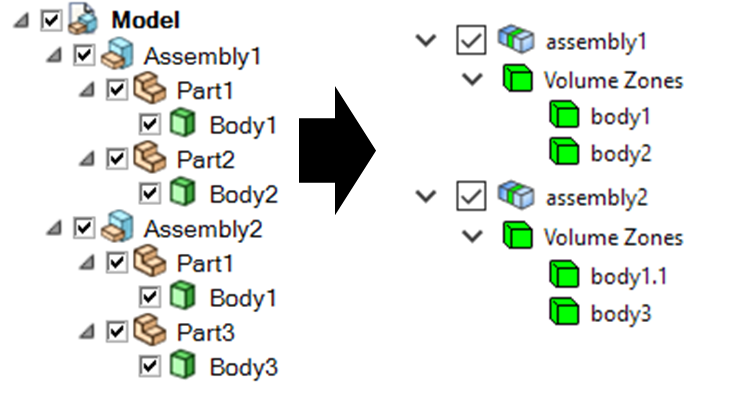
Part creation by assembly (from SpaceClaim to PyPrimeMesh part structure)#
Part#
When you import a CAD model and specify the PartCreationType parameter
as PART, a part per CAD part is created that inherits the part
name from the CAD part name. The number of zones within a part is identical to the number of bodies within the CAD
part.
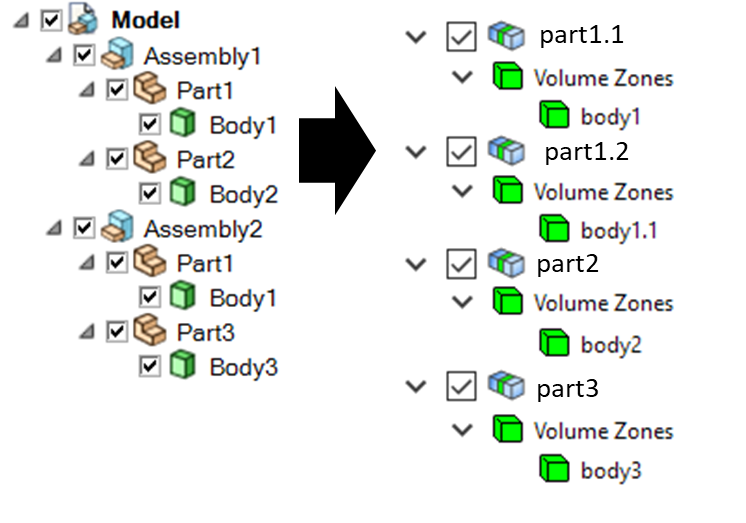
Part creation by part (from SpaceClaim to PyPrimeMesh part structure)#
Body#
When you import a CAD model and specify the PartCreationType parameter
as BODY, a part per CAD body is created that inherits the part name
from the CAD body name. The number of parts is identical to the number of bodies.
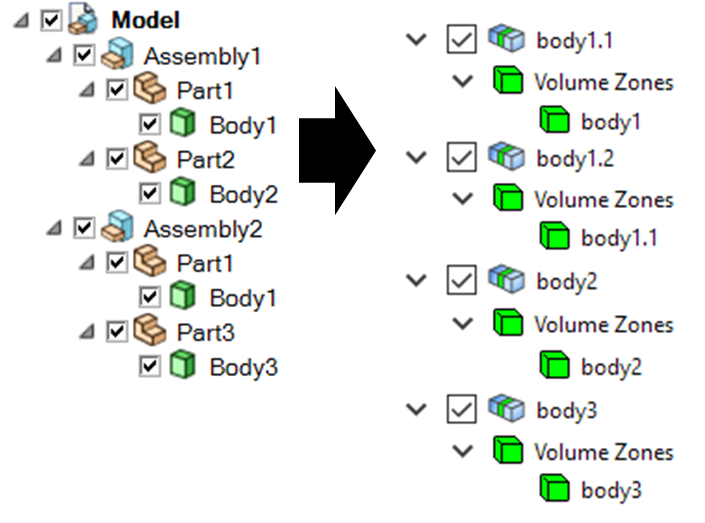
Part creation by body (from SpaceClaim to PyPrimeMesh part structure)#
Import and export solver mesh files#
Tip
File extensions such as CAS (*.cas), MSH (*.msh, *.msh.gz), and CDB (*.cdb) can be imported
using the Mesh.read() method and exported using the
Mesh.write() method in the Lucid API.
Import solver mesh files#
The
FileIO.import_fluent_case()method allows you to import Fluent case(*.cas, *.cas.gz, *.cas.h5)files and set parameters for importing files using theImportFluentCaseParamsclass.The
FileIO.import_fluent_meshing_meshes()method allows you to import Fluent Meshing’s mesh files(*.msh, *.msh.gz)and set parameters for importing files using theImportFluentMeshingMeshParamsclass. You can import multiple files in parallel using multithreading with the optionalenable_multi_threadingparameter.The
FileIO.import_mapdl_cdb()method allows you to import MAPDL(*.cdb)files and set parameters for importing files using theImportMapdlCdbParamsclass. You can import quadratic mesh elements as linear with the optionaldrop_mid_nodesparameter.
Note
All import methods have the optional parameter to append imported files to an existing model.
Export solver mesh files#
The
FileIO.export_fluent_case()method allows you to export Fluent case(*.cas, *.cas.gz, *.cas.h5)files and set parameters for exporting files using theExportFluentCaseParamsclass.The
FileIO.export_fluent_meshing_meshes()method allows you to export Fluent Meshing’s mesh(*.msh)files and set parameters for exporting files using theExportFluentMeshingMeshParamsclass.The
FileIO.export_mapdl_cdb()method allows you to export MAPDL(*.cdb)files and set parameters for exporting files using theExportMapdlCdbParamsclass.The
FileIO.export_boundary_fitted_spline_kfile()method allows you to export IGA LS-DYNA keyword(*.k)files and set parameters for exporting boundary-fitted splines using theExportBoundaryFittedSplineParamsclass.The
FileIO.export_lsdyna_keyword_file()function allows you to write out an LS-DYNA Keyword(*.k)file that contains the mesh definition and other necessary information to carry out the analysis run by the LS-DYNA solver. TheExportLSDynaKeywordFileParamsclass allows you to specify the application type (SEATBELT, DOORSLAM), indicate whether to compute the spot weld thickness, append the material cards in the K file, provide the database cards to append in the K file, and specify the LS-DYNA data field format. You should specify the material properties card and the database keywords card in LS-DYNA format.Note
The
FileIO.export_lsdyna_keyword_file()function is a beta API. The behavior and implementation might change in the future.
Read and write size field files#
Native PSF format#
The
FileIO.read_size_field()method allows you to read Ansys Prime Server’s size field(*.psf, *.psf.gz)file and set parameters for reading this file using theReadSizeFieldParamsclass.The
FileIO.write_size_field()method allows you to write Ansys Prime Server’s size field(*.psf)file and set parameters for writing this file using theWriteSizeFieldParamsclass. You can write only active size fields into the file with the optionalwrite_only_active_size_fieldsparameter.
Fluent Meshing format#
The FileIO.import_fluent_meshing_size_field()
method allows you to import Fluent Meshing’s size field (*.sf, *.sf.gz) file.

