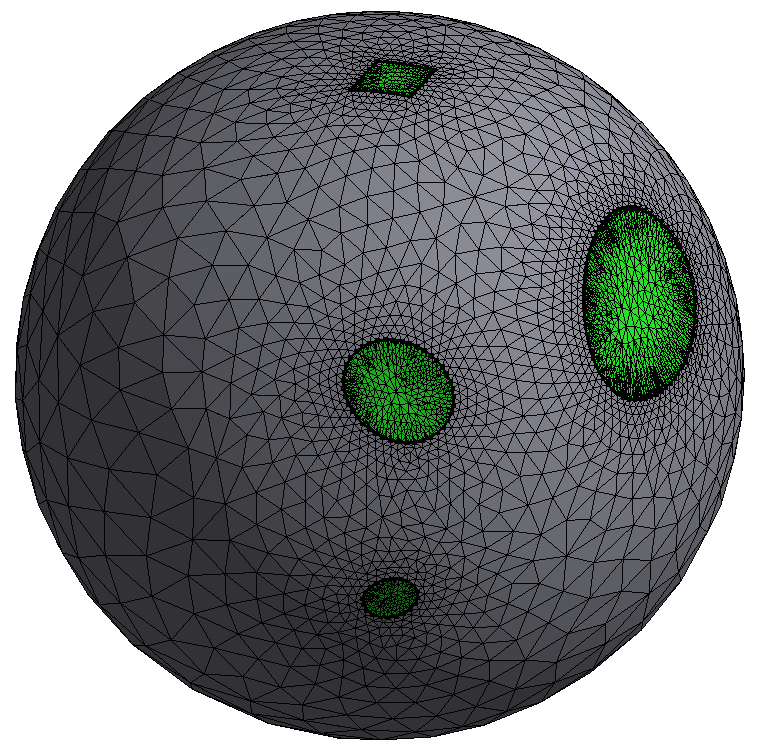
Surface wrapping#
Geometries migrated from various CAD packages often contain gaps and overlaps between the surfaces due to algorithm and tolerance differences of the CAD packages. Surface wrapping provides the ability to create reliable meshes for such geometries without extensive manual clean up and reduces the time required for preprocessing.
The Wrapper class allows you to extract a closed watertight surface used to create a volume mesh from geometry where the inputs:
Are not connected with overlaps
Have holes, leaks, or gaps
Have small features that need to be ignored or walked over
The wrapping operation uses an appropriate material point to identify the relevant surfaces of the selected objects. A coarse Cartesian grid is overlaid on the selected objects to create a contiguous region. This Cartesian grid is used to automatically clean the input geometry and to create the watertight representation. The Cartesian grid is then refined based on the size functions to better represent the selected objects. The intersection between the Cartesian grid and the input geometry is calculated and the intersecting cells are identified and marked.
A watertight faceted representation (defined by quad faces of the Cartesian mesh) is created of the boundaries between the regions of interest (identified via material points) and all other regions. The nodes on the faceted representation are then projected back to the input geometry, resulting into a wrapper surface closely representing the input geometry. The edges are imprinted on the wrapped zones, and individual zones are recovered and rezoned based on the original geometry objects.
The wrapper surface quality is improved by post-wrapping operations. Surfaces are remeshed based on size functions or the size field.
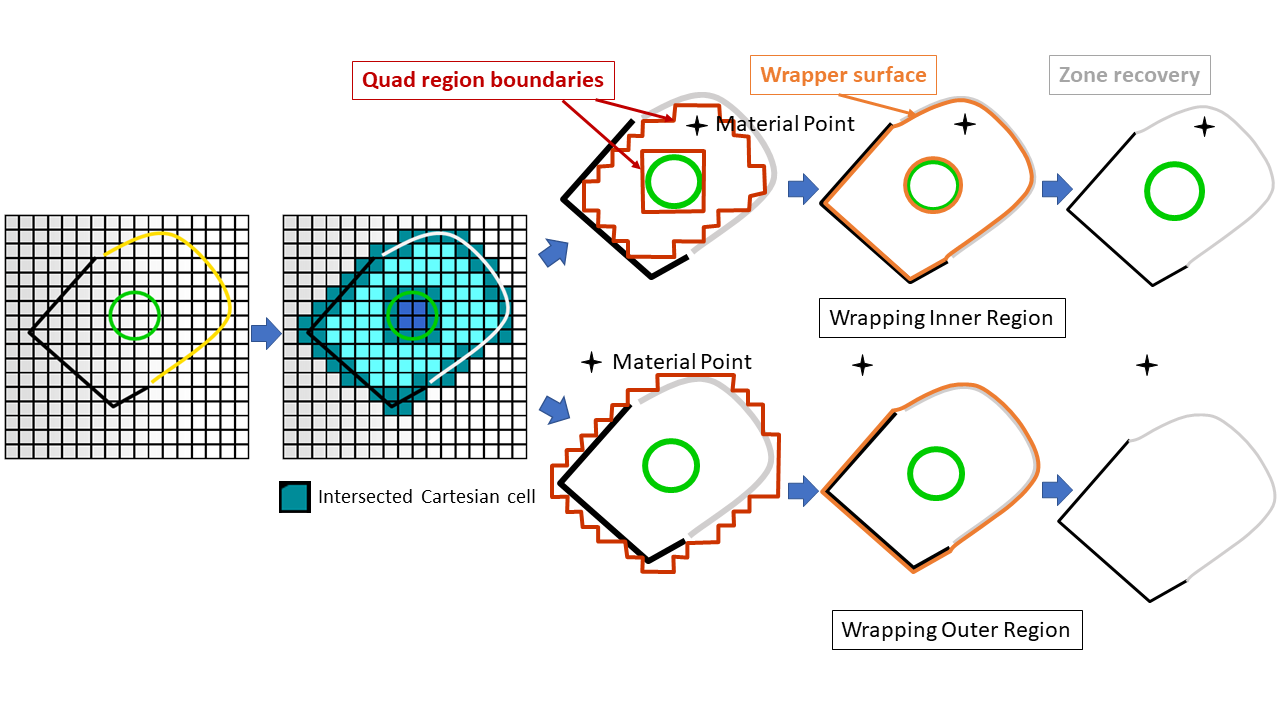
Schematic representation of wrapping process#
The basic PyPrimeMesh wrapper-based workflow follows these steps:
Import the geometry.
model = prime_client.model
input_file = r"D:/PyPrimeMesh/cylinder_with_flange.pmdat"
file_io = prime.FileIO(model)
file_io.read_pmdat(input_file, prime.FileReadParams(model=model))
Define global sizing parameters and size controls with curvature refinement. Sizes are used for wrapper Octree construction.
model.set_global_sizing_params(
prime.GlobalSizingParams(model=model, min=0.2, max=3.0, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(
sizing_type=prime.SizingType.CURVATURE
)
size_control.set_curvature_sizing_params(
prime.CurvatureSizingParams(model=model, min=0.2, max=1.0, normal_angle=18.0)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("curv_global")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model, part_expression="*"))
Define the material points. Material points are used to define fluid regions or seal regions depending on whether the status is
LIVEorDEAD. A 3D coordinate describes the position of the material point.
model.material_point_data.create_material_point(
suggested_name="Mpt",
coords=[20.0, -76.0, -6.0],
params=prime.CreateMaterialPointParams(
model=model, type=prime.MaterialPointType.LIVE
),
)
Create the wrapper control. The scope refers to which entities should be wrapped.
wrapper_control = model.control_data.create_wrapper_control()
wrapper_control.set_suggested_name("cyl_flange_control")
wrapper_control.set_suggested_wrapper_part_name("Wrap_cyl_flange")
wrapper_control.set_geometry_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
part_expression="flange,pipe",
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.FACEANDEDGEZONELETS,
)
)
wrapper_control.set_live_material_points(["Mpt"])
Extract features with angle and face zonelets boundary for feature capture.
features = prime.FeatureExtraction(model)
feature_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model, part_expression="*")
face_zonelets_prime_array = model.control_data.get_part_zonelets(scope=feature_scope)
for item in face_zonelets_prime_array:
features.extract_features_on_face_zonelets(
part_id=item.part_id,
face_zonelets=item.face_zonelets,
params=prime.ExtractFeatureParams(
model=model,
feature_angle=40.0,
label_name="extracted_features",
replace=True,
),
)
Add feature recovery control.
feature_params = prime.FeatureRecoveryParams(
model=model,
scope=prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model, part_expression="*", label_expression="extracted_features"
),
)
wrapper_control.set_feature_recoveries([feature_params])
Wrap the model.
wrapper = prime.Wrapper(model=model)
wrap_params = prime.WrapParams(model, size_control_ids=[size_control.id])
res = wrapper.wrap(wrapper_control_id=wrapper_control.id, params=wrap_params)
wrapper_part = model.get_part(res.id)
Apply diagnostics to compute free edges, multi edges, self-intersections, and duplicate faces after wrap. For more information, see Mesh diagnostics.
Remesh the model. For more information, see Surface meshing.
Note
You can import Fluent Meshing’s size field file for remesh. For more information, see Reading and writing files.
size_control2 = model.control_data.create_size_control(
sizing_type=prime.SizingType.HARD
)
size_control2.set_hard_sizing_params(prime.HardSizingParams(model=model, min=0.8))
size_control2.set_scope(
prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
part_expression="*",
entity_type=prime.ScopeEntity.FACEANDEDGEZONELETS,
)
)
SF1 = prime.SizeField(model)
SF1.compute_volumetric(
[size_control2.id],
prime.VolumetricSizeFieldComputeParams(model=model, enable_multi_threading=False),
)
fz1 = wrapper_part.get_face_zonelets()
ez1 = wrapper_part.get_edge_zonelets_of_label_name_pattern(
label_name_pattern="___wrapper_feature_path___",
name_pattern_params=prime.NamePatternParams(model=model),
)
rem1 = prime.Surfer(model)
surfer_params = rem1.initialize_surfer_params_for_wrapper()
surfer_params.size_field_type = prime.SizeFieldType.VOLUMETRIC
rem1.remesh_face_zonelets(
wrapper_part.id, face_zonelets=fz1, edge_zonelets=ez1, params=surfer_params
)
Improve surface quality and resolve connectivity issues.
wrapper.improve_quality(
part_id=wrapper_part.id,
params=prime.WrapperImproveQualityParams(model=model, target_skewness=0.9),
)
Patch flow region#
This is a beta feature. API behavior and implementation might change in the future.
The Patch Flow Region class creates
patching face zonelets for holes below a specified size
that exist between regions defined by live and dead material points. You can define
multiple dead regions but only one live region can be defined.
The WrapperPatchFlowRegionsParams class allows you to specify the base size and dead regions to create the patched surface.
When you do not provide the base size, the global minimum size value is used.
The patched surface is created towards the dead material point region.
When you create a patched surface, the mesh created is non-conformal.
You may have to perform wrapping to create a conformal mesh.
The following example demonstrates how to patch surfaces using dead and live material points.
Import the model.
file_io = prime.FileIO(model)
res = file_io.read_pmdat(
r"E:\test2\Surface_mesh_1.pmdat", prime.FileReadParams(model=model)
)
g = Graphics(model)
g()
set_num_of_threads = model.set_num_threads(8)
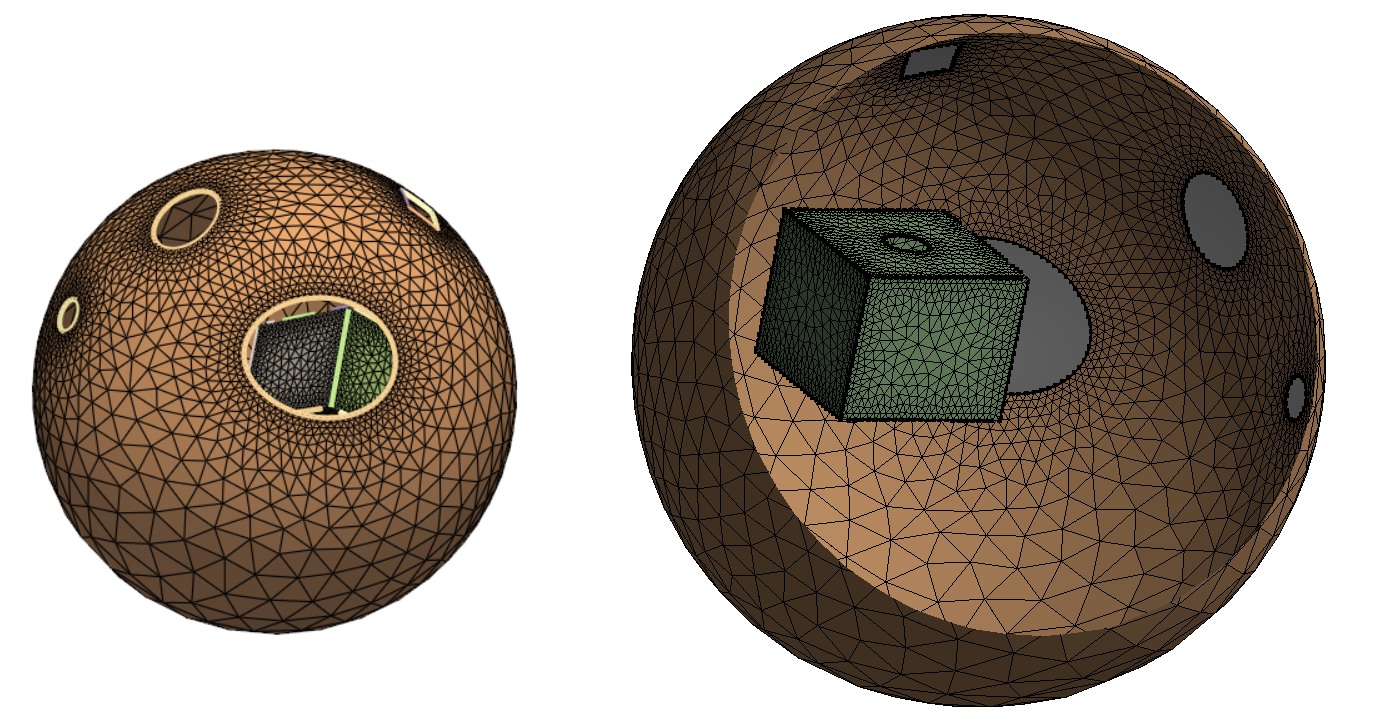
Set the global sizing parameters. If you do not specify the base size, the value for the global minimum size is used.
model.set_global_sizing_params(
prime.GlobalSizingParams(
model,
min=0.5,
max=30,
growth_rate=1.2,
)
)
sfparams = model.get_global_sizing_params()
Create the material points and define the type.
model.material_point_data.create_material_point(
suggested_name="Fluid",
coords=[-13, 62, -24],
params=prime.CreateMaterialPointParams(
model=model,
type=prime.MaterialPointType.LIVE,
),
)
model.material_point_data.create_material_point(
suggested_name="dead_1",
coords=[2, 43, 0.0],
params=prime.CreateMaterialPointParams(
model=model,
type=prime.MaterialPointType.DEAD,
),
)
model.material_point_data.create_material_point(
suggested_name="dead_2",
coords=[11, 60, -8.5],
params=prime.CreateMaterialPointParams(
model=model,
type=prime.MaterialPointType.DEAD,
),
)
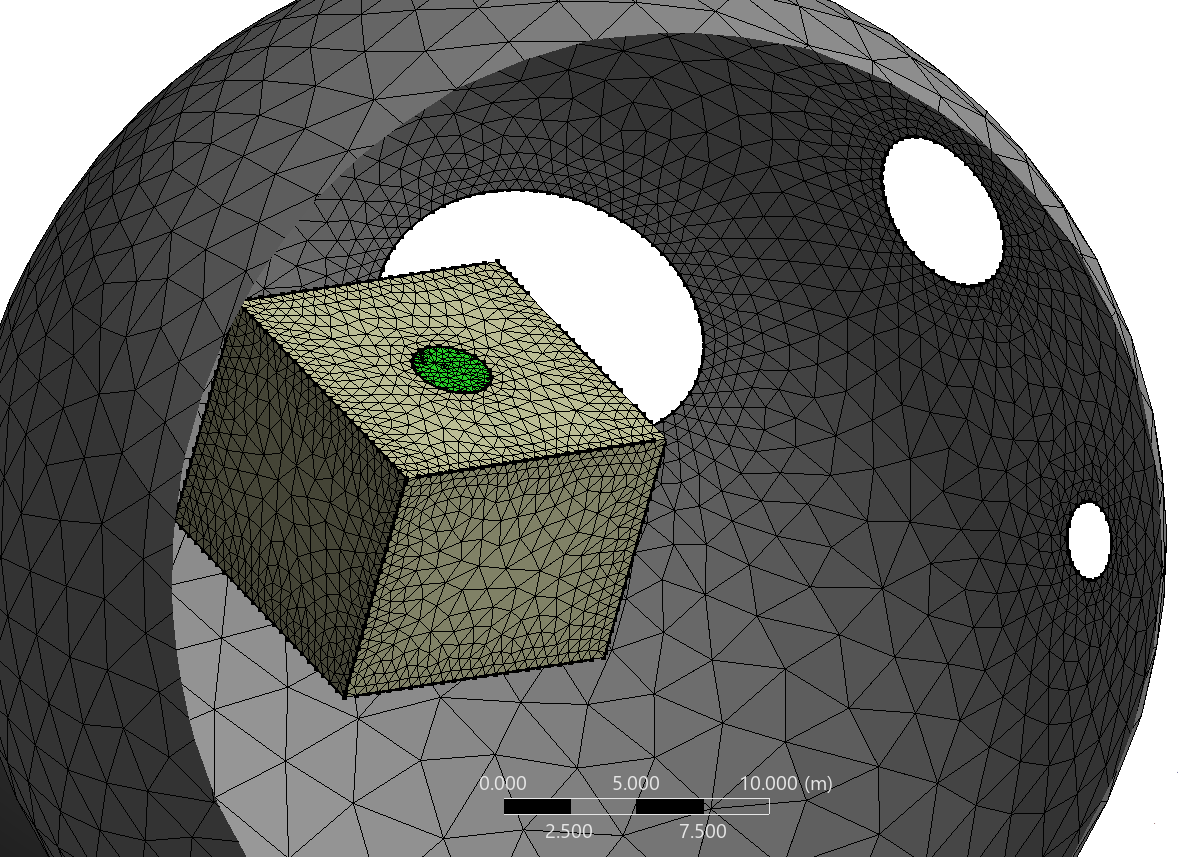
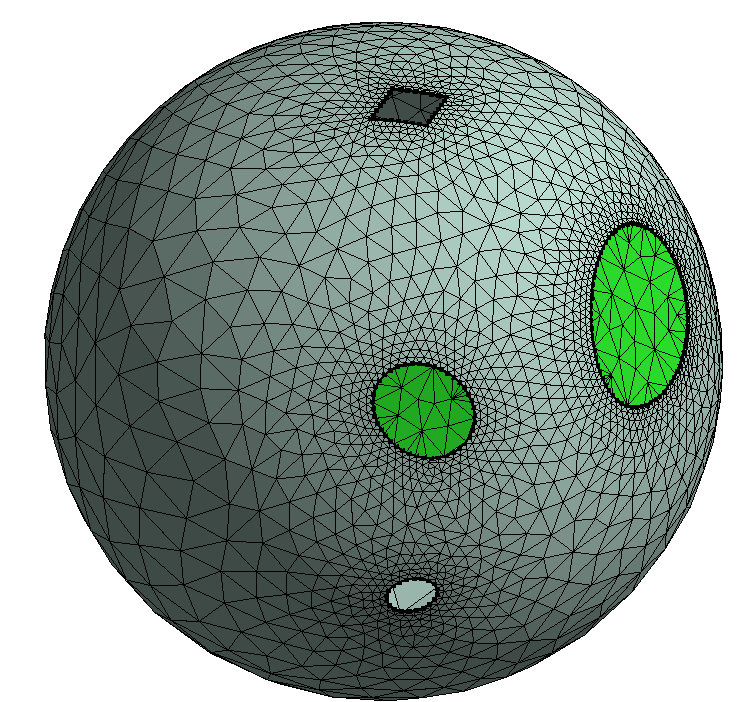
Define the scope, dead region, live region and specify the hole size, base size to be patched to perform patching.
The following image shows the defined dead material points and live material points in the model.
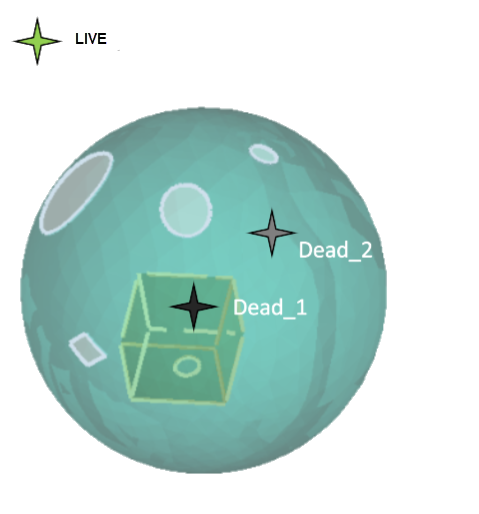
Case 1: scope Dead_1, LIVE material points and specify the hole size to perform patching.
dead_region_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
part_expression="box, sph",
)
faces = model.control_data.get_scope_face_zonelets(
scope=dead_region_scope,
params=prime.ScopeZoneletParams(model),
)
dead_region = prime.DeadRegion(
model=model,
face_zonelet_ids=faces,
dead_material_points=["Dead_1"],
hole_size=5,
)
patch_params = prime.WrapperPatchFlowRegionsParams(
model=model,
dead_regions=[dead_region],
number_of_threads=12,
suggested_part_name="hole_patch_1",
)
wrapper = prime.Wrapper(model=model)
patch_result = wrapper.patch_flow_regions(
live_material_point="LIVE",
params=patch_params,
)
Case 2: scope Dead_2, LIVE material points and specify the hole size and base size to perform patching.
dead_region_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
part_expression="box, sph",
)
faces = model.control_data.get_scope_face_zonelets(
scope=dead_region_scope,
params=prime.ScopeZoneletParams(model),
)
dead_region = prime.DeadRegion(
model=model,
face_zonelet_ids=faces,
dead_material_points=["Dead_2"],
hole_size=15,
)
patch_params = prime.WrapperPatchFlowRegionsParams(
model=model,
base_size=4,
dead_regions=[dead_region],
number_of_threads=12,
suggested_part_name="hole_patch_2",
)
wrapper = prime.Wrapper(model=model)
patch_result = wrapper.patch_flow_regions(
live_material_point="LIVE",
params=patch_params,
)
Case 3: scope Dead_1, Dead_2 and LIVE material points and specify the hole size and base size to perform patching.
dead_region_scope = prime.ScopeDefinition(
model=model,
part_expression="box, sph",
)
faces = model.control_data.get_scope_face_zonelets(
scope=dead_region_scope,
params=prime.ScopeZoneletParams(model),
)
dead_region = prime.DeadRegion(
model=model,
face_zonelet_ids=faces,
dead_material_points=["Dead_1", "Dead_2"],
hole_size=15,
)
patch_params = prime.WrapperPatchFlowRegionsParams(
model=model,
base_size=2,
dead_regions=[dead_region],
number_of_threads=8,
suggested_part_name="hole_patch_3",
)
wrapper = prime.Wrapper(model=model)
patch_result = wrapper.patch_flow_regions(
live_material_point="LIVE",
params=patch_params,
)