Volume sweeping#
The VolumeSweeper class creates a volume mesh on 2.5D models, stacking faces
or edge zonelets one above the other in layers. This volume sweeping technology stacks each of the input topovolumes individually.
Note
A 2.5D or stackable geometry is any closed volume or set of closed volumes that can be obtained by successive extrusion of a series of 2D geometries, along the area normal of the 2D geometries.
A geometry is stackable only when there is a direction called stacking direction, to which all surfaces are either perpendicular or parallel.
Warning
The hex-dominant mesh created by volume sweeper can only be applied to 2.5D models. Only conformal mesh within a part is supported.
Volume sweeping workflow involves the following:
Create imprints of model edges on the base face.
Surface mesh the imprinted base face.
Extrude the base face mesh at the selected origin by stacking the face layer by layer along the specified direction to generate a volume mesh.
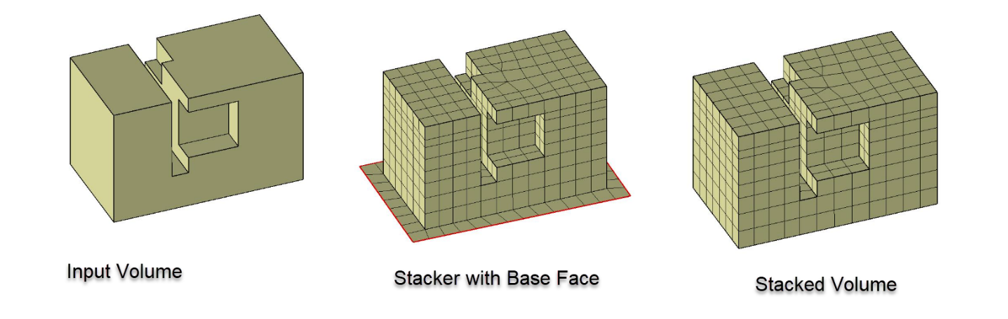
Example of Volume Sweeping Workflow#
Hex-dominant meshing for 2.5D geometry#
The following example shows how to mesh a thin disc using volume sweeper:
# Set the global sizing parameters after importing the model
model.set_global_sizing_params(
prime.GlobalSizingParams(model=model, min=0.15, max=0.5, growth_rate=1.2)
)
model.delete_volumetric_size_fields(model.get_active_volumetric_size_fields())
part = model.parts[0]
Define stacking parameters:
Set origin and direction vector for stacking orientation
Option to set defeaturing tolerance for edge imprints
Option to set maximum stack size allowed for stacking
Option to delete base face after stacking
Note
Default global max size is used for stacking parameters if you are not providing the max size.
Default lateral_defeature_tolerance and stacking_defeature_tolerance are set to (global min size/4).
sweeper = prime.VolumeSweeper(model)
stacker_params = prime.MeshStackerParams(
model=model, direction=[0.0, 1.0, 0.0], max_offset_size=0.5, delete_base=True
)
Print the results of stacking parameters so that you can review them:
>>> print(stacker_params)
origin : [0. 0. 0.]
direction : [0. 1. 0.]
lateral_defeature_tolerance : 0.0375
stacking_defeature_tolerance : 0.0375
max_offset_size : 0.5
size_control_ids : []
delete_base : True
Create base face:
createbase_results = sweeper.create_base_face(
part_id=part.id, topo_volume_ids=part.get_topo_volumes(), params=stacker_params
)
base_faces = createbase_results.base_face_ids
Warning
The topovolume cannot have meshed topofaces.
Compute volumetric size field and perform surface meshing on the base face:
size_field = prime.SizeField(model)
res = size_field.compute_volumetric(
size_control_ids=createbase_results.size_control_ids,
volumetric_sizefield_params=prime.VolumetricSizeFieldComputeParams(model),
)
surfer_params = prime.SurferParams(
model=model, size_field_type=prime.SizeFieldType.VOLUMETRIC, generate_quads=True
)
meshbase_result = prime.Surfer(model).mesh_topo_faces(
part_id=part.id, topo_faces=base_faces, params=surfer_params
)
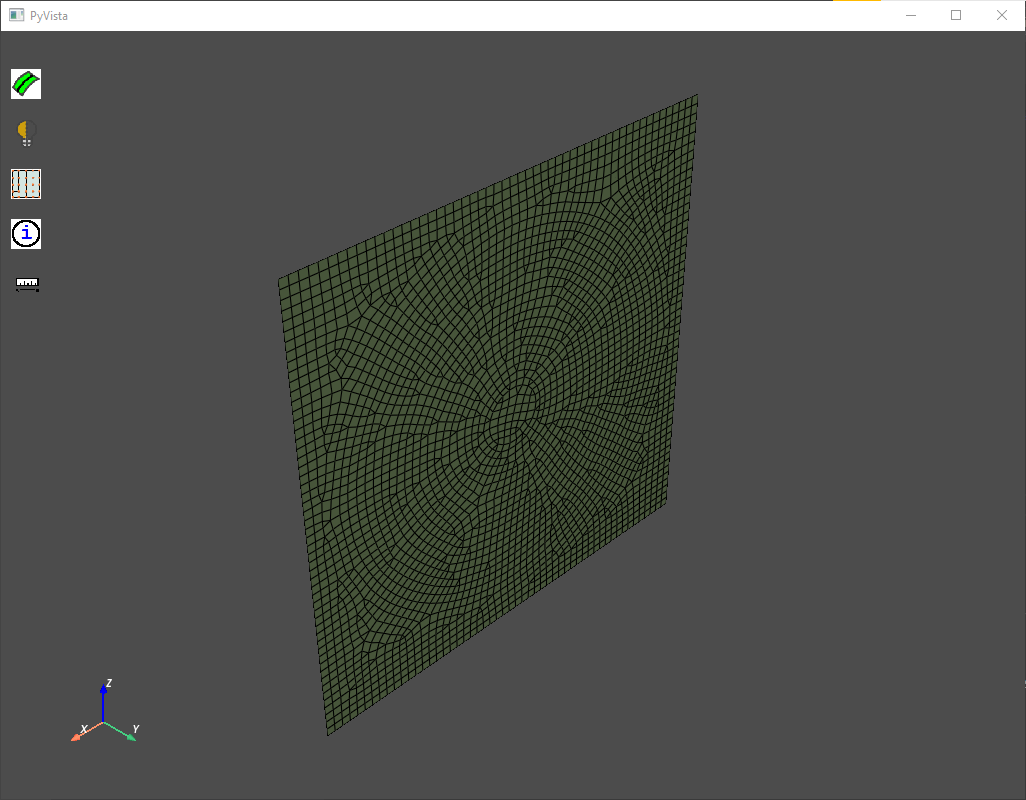
Base face meshed#
Stack the base face:
stackbase_results = sweeper.stack_base_face(
part_id=part.id,
base_face_ids=base_faces,
topo_volume_ids=part.get_topo_volumes(),
params=stacker_params,
)
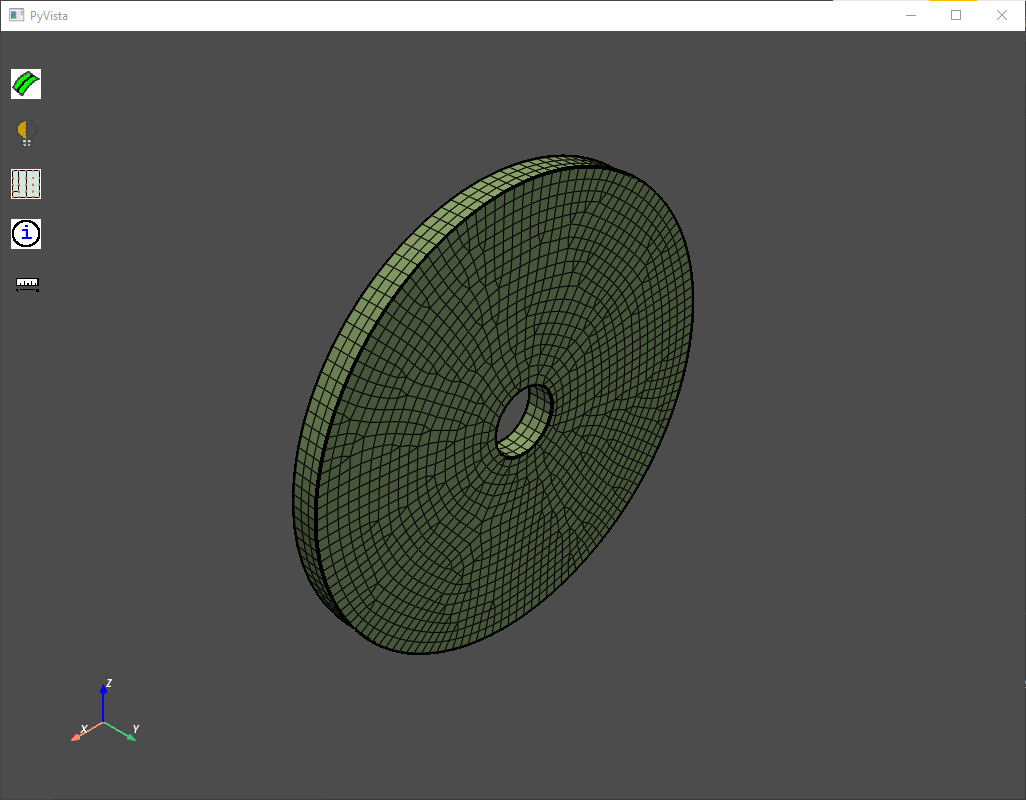
Stack base meshed#