Sizing#
PyPrimeMesh provides various sizing controls to help you define how the mesh size is distributed on a surface or within the volume.
Sizing control#
Mesh quality and resolution are important factors for capturing physics accurately and efficiently. Size controls allows you to get the desired mesh distribution. PyPrimeMesh specifies the sizing requirements using sizing controls. The sizing controls in PyPrimeMesh have the following:
Scope
Maximum rate of change of size
Range within which the sizes should be on or within the scope
The SizingType class has control types for defining sizing requirements:
Curvature
Proximity
Hard
Soft
Meshed
Body of influence
Curvature sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the CURVATURE
parameter sizes based on the scope on the local curvature. The size is small when the local curvature is large and vice versa.
This code shows how to use the CurvatureSizingParams class to specify
the minimum and maximum size, growth rate, and normal angle:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.CURVATURE)
size_control.set_curvature_sizing_params(
prime.CurvatureSizingParams(model=model, min=0.2, max=2.0, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("curv_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))
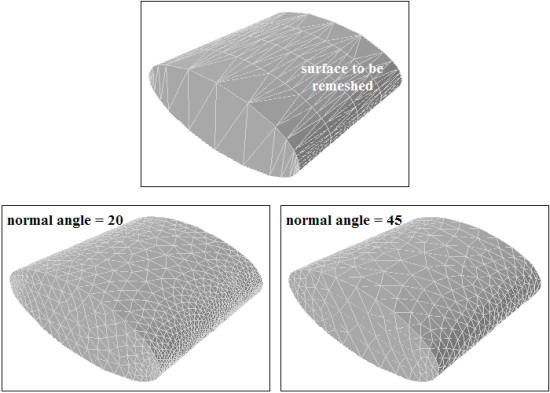
The normal angle parameter is the maximum allowable angle that one element edge may span. For example, a value of 5 implies that a division are made when the angle change along the curve is 5 degrees. Hence, a 90 degree arc is divided into approximately 18 segments.
Proximity sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the
PROXIMITY parameter sizes based on the closeness of
the surfaces or edges specified in the scope. This code shows how to use the
ProximitySizingParams class to specify the
minimum and maximum size, growth rate, and the number of element per gap:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.PROXIMITY)
size_control.set_proximity_sizing_params(
prime.ProximitySizingParams(
model=model,
min=0.1,
max=2.0,
growth_rate=1.2,
elements_per_gap=3.0,
ignore_orientation=True,
ignore_self_proximity=False,
)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("prox_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))
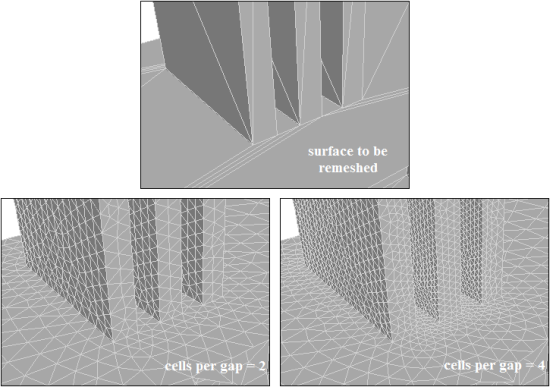
The ignore_self_proximity
and ignore_orientation
parameters are also considered for proximity sizing. The ignore_self_proximity parameter
is set to True if proximity between faces in the same face zonelet is to be ignored. The
ignore_orientation parameter allows you to ignore the face normal orientation during the
proximity calculation. This Boolean parameter is set to False by default. In general,
the proximity depends on the direction of face normals.
This example explains the use of the ignore_orientation parameter for face proximity.
The normals on the grooved box point inward. With the default setting of False, the
proximity size function does not refine the surface along the entire groove length.
If the ignore_orientation is set to True, the surface is refined along the groove length

Hard sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the
HARD parameter sizes on the scope based on a uniform
value while meshing. This code shows how to use the HardSizingParams
class to specify the minimum size and growth rate:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.HARD)
size_control.set_hard_sizing_params(
prime.HardSizingParams(model=model, min=0.2, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("hard_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))
Soft sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the
SOFT parameter sizes on the scope based on a
certain maximum value that should not be exceeded while meshing. This code shows how
to use the SoftSizingParams class to specify
the maximum size and growth rate:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.SOFT)
size_control.set_soft_sizing_params(
prime.SoftSizingParams(model=model, max=0.2, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("soft_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))

Meshed sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the
MESHED parameter sizes based on existing local sizes.
This example shows how to use the MeshedSizingParams
class to specify the growth rate:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.MESHED)
size_control.set_meshed_sizing_params(
prime.MeshedSizingParams(model=model, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("meshed_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))
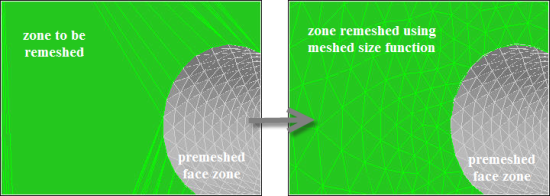
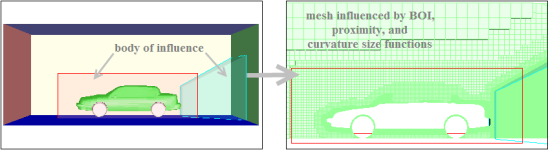
Body of influence sizing#
In the SizingType class, selecting the
BOI parameter sizes inside a closed volume scope
that is not to exceed a certain maximum value. This code shows how to use the
BoiSizingParams class to specify the maximum size and growth rate:
size_control = model.control_data.create_size_control(prime.SizingType.BOI)
size_control.set_boi_sizing_params(
prime.BoiSizingParams(model=model, max=20.0, growth_rate=1.2)
)
size_control.set_suggested_name("BOI_control")
size_control.set_scope(prime.ScopeDefinition(model=model))
Size fields#
The SizeFieldType class helps you to fetch the element size
at a given location. These size field types are available in PyPrimeMesh:
ConstantVolumetricGeodesicGeometricMeshedgeodesic
The Volumetric and Geodesic size fields can process and respect the size control that you define.
The Volumetric size field can be computed using the Compute volumetric
method and then surface and volume meshing can be applied. The remaining size field types are computed as
part of various surface and volume meshing operations.
Constant size field#
In the SizeFieldType class, selecting the
CONSTANT parameter computes the size field
based on the size controls specified.

Volumetric size field#
In the SizeFieldType class, selecting the
VOLUMETRIC parameter computes the size field
based on the size controls specified.
Geodesic size field#
In the SizeFieldType class, selecting the
GEODESIC parameter computes the size field
on face nodes based on the size controls specified. Sizes are defined along a surface rather than
the volume. Geodesic sizing enables you to confine sizes to surfaces and avoid problems like
dead space refinement.


Geometric size field#
In the SizeFieldType class, selecting the
GEOMETRIC parameter computes the size field
based on existing boundary sizes. Sizes can gradually increase from the minimum size to the
maximum size based on the growth rate.
Meshedgeodesic size field#
In the SizeFieldType class, selecting the
MESHEDGEODESIC parameter computes
the size field using average mesh edge lengths and is diffused geodesical.